The action of a disinfectant may be affected by the following factors:
1. Type of microorganisms: the most resistant forms are bacterial and fungal spores. Followed by fungi, Gram-positive cocci, Gram-positive bacilli and Gram-negative bacilli (except Pseudomonas aeruginosa which is particularly resistant to quaternary ammonium-based disinfectants). Lipid-coated viruses are more sensitive than uncoated viruses.
2. Number of microorganisms: if the microbial load is high, a higher amount of disinfectant or a longer exposure time is needed to achieve a certain level of disinfection. Hence the need for pre-cleaning before applying the disinfectant, as this reduces the microbial load and removes organic matter that interferes with the disinfectant action.
3. Exposure time and product concentration: generally, as the contact time increases, the lethality rate increases. Contact time is a very critical factor in ensuring disinfection. To determine bacterial lethality to disinfectants, the experimental time of choice is 5 minutes, although this may vary.
4. Organic matter: Interferes with the action of the disinfectant because it inactivates certain disinfectants, e.g. bleach, and can also form a protective barrier for micro-organisms.
5. Other substances: soaps and detergents, cork, cotton, etc. may react with the disinfectant and neutralise it.
6. Surface of action: The main limitation of disinfection systems lies in the problems of access to areas with grooves, cracks, blind spots, corrosion spots. Irregularities in surfaces allow microbes and organic matter to lodge and therefore need to be cleaned thoroughly, balancing the intensity of cleaning with the maintenance of utensils. The choice of materials, e.g. stainless steel, and the treatment of these materials in order to retain as few bacteria as possible after cleaning and disinfection is crucial to ensure the hygiene of surfaces and thus avoid cross-contamination.
7. Temperature: the chemical effects of cleaning and disinfection increase linearly with temperature and almost double for every 10°C increase, the effectiveness being proportional until reaching temperatures at which cell death is induced.
8. Biofilms: When microorganisms colonise a surface and adhere to it, they begin to multiply and organise themselves into communities called biofilms, which are more resistant to disinfectants because they are embedded in a matrix of exopolysaccharides that gives them stability, nutrition and resistance to antimicrobial substances.
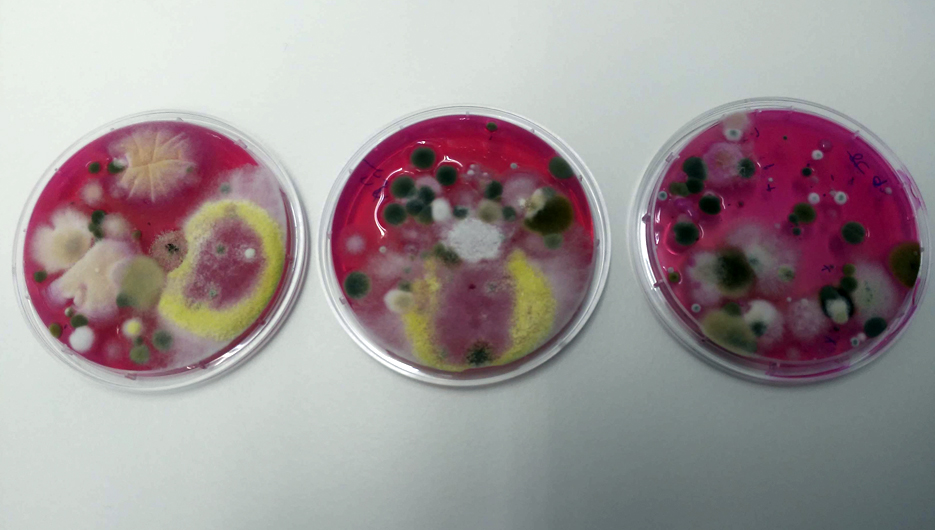
To make sure that the cleanliness and disinfection of surfaces involved in food handling and production processes is optimal, it is necessary to check them with surface controls. Clean-Biotec provides environmental controls of air and surfaces for microbiological indicators for all links in the food chain and sanitary environments.
More information:
Clean-Biotec
laboratorio@clean-biotec.com
(+34) 941 238 261
www.clean-biotec.com


